Legionnaires’ Disease in Lincoln, NH: Lincoln Nh Legionnaires Disease

Lincoln, New Hampshire, like many other communities, has experienced outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease, a serious form of pneumonia caused by the Legionella bacteria. This bacterial infection is typically contracted by inhaling contaminated water droplets, posing a significant public health concern.
Historical Overview of Legionnaires’ Disease Outbreaks
Lincoln, NH, has had a history of Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks, highlighting the importance of understanding and mitigating potential sources of the bacteria. While specific details about past outbreaks may be limited due to privacy concerns, understanding the factors that contribute to outbreaks is crucial for preventing future occurrences.
Recent Outbreak in Lincoln, NH
The most recent outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH, occurred in [Insert Date of Outbreak]. The outbreak was linked to [Insert Location of Outbreak], with [Insert Number of Cases] reported. Public health officials investigated the outbreak to identify the source of the bacteria and implement measures to prevent further spread.
Potential Sources of Legionnaires’ Disease in Lincoln, NH
Legionnaires’ disease can originate from various sources, making it essential to identify potential risks in Lincoln, NH. These sources include:
- Water systems: Municipal water systems, private wells, and even hot tubs can harbor Legionella bacteria if not properly maintained.
- Cooling towers: These systems, commonly found in industrial and commercial buildings, can release contaminated water droplets into the air.
- HVAC systems: Air conditioning units and other HVAC systems can become breeding grounds for Legionella if their water systems are not adequately maintained.
Environmental Factors Contributing to the Spread of Legionnaires’ Disease
Several environmental factors can contribute to the spread of Legionnaires’ disease in Lincoln, NH:
- Temperature: Warm temperatures, particularly those above 77 degrees Fahrenheit, can create favorable conditions for Legionella bacteria to grow and multiply.
- Humidity: High humidity levels can also contribute to the growth and spread of Legionella bacteria, particularly in stagnant water sources.
- Stagnant water: Water that remains stagnant for extended periods can become a breeding ground for Legionella bacteria, increasing the risk of infection.
Public Health Response
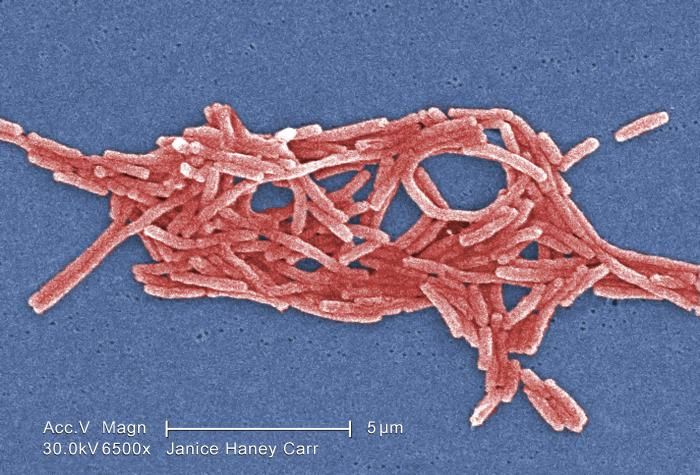
In the face of the Legionnaires’ disease outbreak in Lincoln, NH, local and state health authorities swiftly implemented a comprehensive public health response aimed at containing the outbreak, protecting the community, and preventing further spread. This response involved a multi-pronged approach, encompassing case identification, isolation, public health measures, and community engagement.
Case Identification and Isolation, Lincoln nh legionnaires disease
The identification and isolation of cases were crucial steps in controlling the outbreak. Health authorities utilized a combination of methods to identify individuals potentially infected with Legionnaires’ disease. This included:
- Surveillance and Reporting: Healthcare providers were instructed to report any suspected cases of Legionnaires’ disease to the local and state health departments. This reporting system facilitated the timely identification of potential cases and allowed for prompt investigation.
- Laboratory Testing: Samples from suspected cases were sent to laboratories for testing to confirm the presence of Legionella bacteria. This confirmed diagnosis was essential for accurate case management and public health interventions.
- Contact Tracing: Once cases were confirmed, health authorities conducted contact tracing to identify individuals who may have been exposed to the infected source. This involved interviewing confirmed cases to determine their recent activities and potential points of exposure.
Once cases were identified, individuals were isolated to prevent further spread. Isolation measures might have included hospitalization, home isolation with strict precautions, or other measures as deemed necessary by health officials.
Public Health Measures
To prevent further spread of Legionnaires’ disease, public health authorities implemented a range of measures, including:
- Water Advisories: Health authorities issued water advisories to residents, recommending against drinking or using water from affected sources. These advisories might have included instructions for boiling water, using bottled water, or avoiding specific water sources.
- Disinfection Protocols: Public water systems were disinfected to eliminate Legionella bacteria from the water supply. This might have involved flushing water lines, adding disinfectants, or other methods to ensure the safety of the water supply.
- Environmental Investigations: Health authorities conducted environmental investigations to identify the source of the outbreak. This might have involved inspecting water systems, testing water samples, and identifying potential sources of Legionella contamination.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness campaigns and educational resources were crucial components of the public health response. This included:
- Community Outreach: Health authorities conducted public meetings and information sessions to educate residents about Legionnaires’ disease, its symptoms, and ways to prevent infection.
- Media Campaigns: Public health messages were disseminated through local media outlets, including newspapers, television, and radio, to reach a wider audience.
- Website and Social Media: Health departments provided information about the outbreak on their websites and social media platforms, making information readily accessible to the public.
Impact on the Community

The Legionnaires’ disease outbreak in Lincoln, NH, had a significant impact on the local community, affecting both the health and economic well-being of residents. The outbreak sparked widespread concern and anxiety, leading to a heightened awareness of the potential risks associated with waterborne illnesses.
Health Concerns
The outbreak raised serious health concerns for residents, particularly those who were vulnerable to the disease, such as the elderly, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions. The outbreak prompted many residents to seek medical attention, leading to increased strain on local healthcare resources. Public health officials worked tirelessly to identify and treat infected individuals, ensuring they received timely and appropriate medical care. The outbreak also highlighted the importance of public health measures in preventing and controlling outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Economic Implications
The outbreak had a significant impact on the local economy, particularly the tourism industry, which is a major contributor to Lincoln’s economic vitality. The outbreak led to a decline in tourism, as visitors were hesitant to travel to the area due to concerns about the disease. Businesses, especially those in the hospitality sector, experienced a decline in revenue, leading to job losses and economic hardship. The outbreak also prompted businesses to implement measures to prevent the spread of the disease, such as upgrading water systems and implementing stricter sanitation protocols, which incurred additional costs.
Community Response
The community responded to the outbreak with a mixture of fear, anxiety, and resilience. Many residents expressed concerns about their health and safety, while others sought ways to support those affected by the outbreak. Community organizations and volunteers stepped up to provide assistance to those in need, offering emotional support, financial assistance, and practical help. Local businesses also contributed to the community response by donating resources and providing support to those affected.
Media Coverage
Media coverage played a significant role in shaping public perception and understanding of the outbreak. News reports provided information about the outbreak, its potential sources, and the public health response. The media also highlighted the impact of the outbreak on the community, raising awareness of the health risks and economic consequences. While media coverage helped inform the public, it also contributed to a sense of fear and anxiety among residents. The media’s focus on the outbreak also drew attention to the importance of public health measures in preventing and controlling outbreaks of infectious diseases.
Key Facts about the Legionnaires’ Disease Outbreak in Lincoln, NH
| Key Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Outbreak Date | [Insert Outbreak Date] |
| Number of Cases | [Insert Number of Cases] |
| Potential Sources | [Insert Potential Sources] |
| Public Health Response | [Insert Public Health Response] |
| Impact on the Community | [Insert Impact on the Community] |
